
Massive parallel processing (MPP) data warehouses like Amazon Redshift scale horizontally by adding compute nodes to increase compute, memory, and storage capacity.

For example, a product dimension may have the brand in a separate table.
Snowflake schemas extend the star concept by further normalizing the dimensions into multiple tables. The fact table has foreign key relationships to one or more dimension tables that contain descriptive attribute information for the sold item, such as customer or product. Star and snowflake schemas organize around a central fact table that contains measurements for a specific event, such as a sold item. You will see many links to the Amazon Redshift Database Developer Guide, which is the authoritative technical reference and has a deeper explanation of the features and decisions highlighted in this post. Last year AWS published an article titled “Optimizing for Star Schemas on Amazon Redshift” that described design considerations when using star schemas.This post replaces that article and shows how interleaved sort keys may affect design decisions when implementing star schemas on Amazon Redshift. Amazon Redshift performs well on common data models like a star or snowflake schema, third normal form (3NF), and denormalized tables. Interleaved sort keys can enhance performance on Amazon Redshift data warehouses, especially with large tables. The Amazon Redshift team has released support for interleaved sort keys, another powerful option in its arsenal for speeding up queries. Customers have moved data warehouses of all types to Amazon Redshift with great success. Many organizations implement star and snowflake schema data warehouse designs and many BI tools are optimized to work with dimensions, facts, and measure groups. Additionally, late binding views can be used with external tables via Redshift Spectrum.Chris Keyser is a Solutions Architect for AWS Using late-binding views in a production deployment of dbt can vastly improve the availability of data in the warehouse, especially for models that are materialized as late-binding views and are queried by end-users, since they won’t be dropped when upstream models are updated. In practice, this means that if upstream views or tables are dropped with a cascade qualifier, the late-binding view does not get dropped as well. This DDL option "unbinds" a view from the data it selects from. Redshift supports views unbound from their dependencies, or late binding views. AWS Documentation » Amazon Redshift » Database Developer Guide » Designing Tables » Choosing Sort Keys.AWS Documentation » Amazon Redshift » Database Developer Guide » Designing Tables » Choosing a Data Distribution Style.
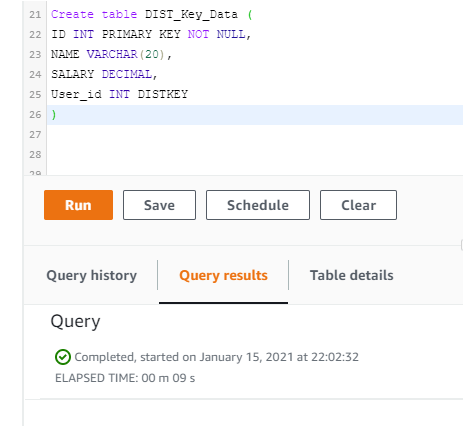
For more information on distkeys and sortkeys, view Amazon's docs:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
